3 Easy tips to Improve The Performance of your PhoneGap/Cordova Application

If you’ve never heard of Phonegap/Cordova and can’t understand what the fuss is about, Phonegap/Cordova is essentially a framework for Hybrid App Development that allows you to build apps for multiple platforms ( iOS, Android, etc ) using simple JavaScript/HTML/CSS code.
Adobe Phonegap & Apache Cordova are essentially the same thing, the only difference is their branding, Phonegap is supported by Adobe and is proprietary software. Whereas Apache Cordova is the open source version of Phonegap. Due to this, these both names can be used interchangeably when describing the framework.
Since Cordova uses Android System Webview, it can be a little slower & less responsive when compared to apps that are completely built using Native Languages ( Java, Kotlin, Swift ). But hey, since Cordova is providing us with so many awesome features and saving us ( the developers ) so much time by allowing us to build apps for multiple platforms using the same code! It isn’t fair to complain about it and say that it’s slow.
That’s why, in this tutorial, we’ll be looking at a few ways to improve the performance of Cordova apps by applying a few fixes here and there. If done right, it can allow you to get the best of both worlds without having to compromise on app performance or development speed
Table of Contents
Phonegap/Cordova vs Native Apps – Performance

Before moving ahead and working on optimizing the Cordova app, let’s have a look at what we are competing against – A Natively Built Application
The Natively built android application is written from the ground up, using only the native language that is prescribed by the Operating System. ( For eg, Java/Kotlin for Android and Swift for iOS ).
Native applications are almost always going to outperform any Hybrid / Cross-Platform application because they are compiled to binary/bytecode and there is no layer between the code and its execution. Whereas frameworks such as Cordova have an intermediate layer ( Webview ) that interacts with the user. This layer slows down the application considerably.
Now there is no way that we can outright remove this intermediate layer and make the application perform better than a Native application. But there are ways to speed up the intermediate layer ( webview ) so that we can reach a performance level comparable to that of a Natively built Android Application.
Cordova vs Other Frameworks ( Xamarin, React Native, etc )

There might be a misconception that all of these languages – multiple platforms frameworks work similarly. But that is not true, even though they offer the same thing, there is a significant difference in how they achieve it.
Most of these frameworks can be classified into two categories
- Hybrid app frameworks
- Cross Platform frameworks
Hybrid App Frameworks
These apps usually have an embedded browser inside them ( System WebView ) and they use this embedded browser to simply show the HTML/CSS/JavaScript code as it is without doing any major modifications at all.
Without any optimizations, there is almost no difference between the performance of a Mobile Browser Website and a hybrid application.
The only significant advantage of building a Hybrid application is that they allow a web app to access the native mobile components ( Vibration sensor, Geolocation sensor, proximity sensor, etc )
Frameworks such as Cordova/Phonegap fit into this category
Cross Platform Frameworks
They are a little different than Hybrid Frameworks, instead of simply displaying the HTML/CSS/JavaScript code as a web application, they compile the Web Components into Native Mobile Components.
For example, a simple HTML heading <h1> is compiled into the Android equivalent known as <TextView> to display the heading.
This compilation improves the performance by a huge margin when compared to Hybrid apps, but they don’t match the level of Native applications as these apps usually still have a Background JavaScript Thread running to process the Data / UI changes.
Frameworks such as React Native & Xamarin fit into this category
How to enhance the performance of a Phonegap/Cordova App?
Now that we have looked at where Cordova stands, it’s time for us to work on improving the speed as much as we can.
But there’s a problem, we can’t improve on something that we cannot measure. That’s why we’ll be using a Benchmarking tool called Jetstream2 to measure the performance of the Cordova Application before and after making performance-improving changes
Let’s create a new Cordova application and measure the performance without any optimizations
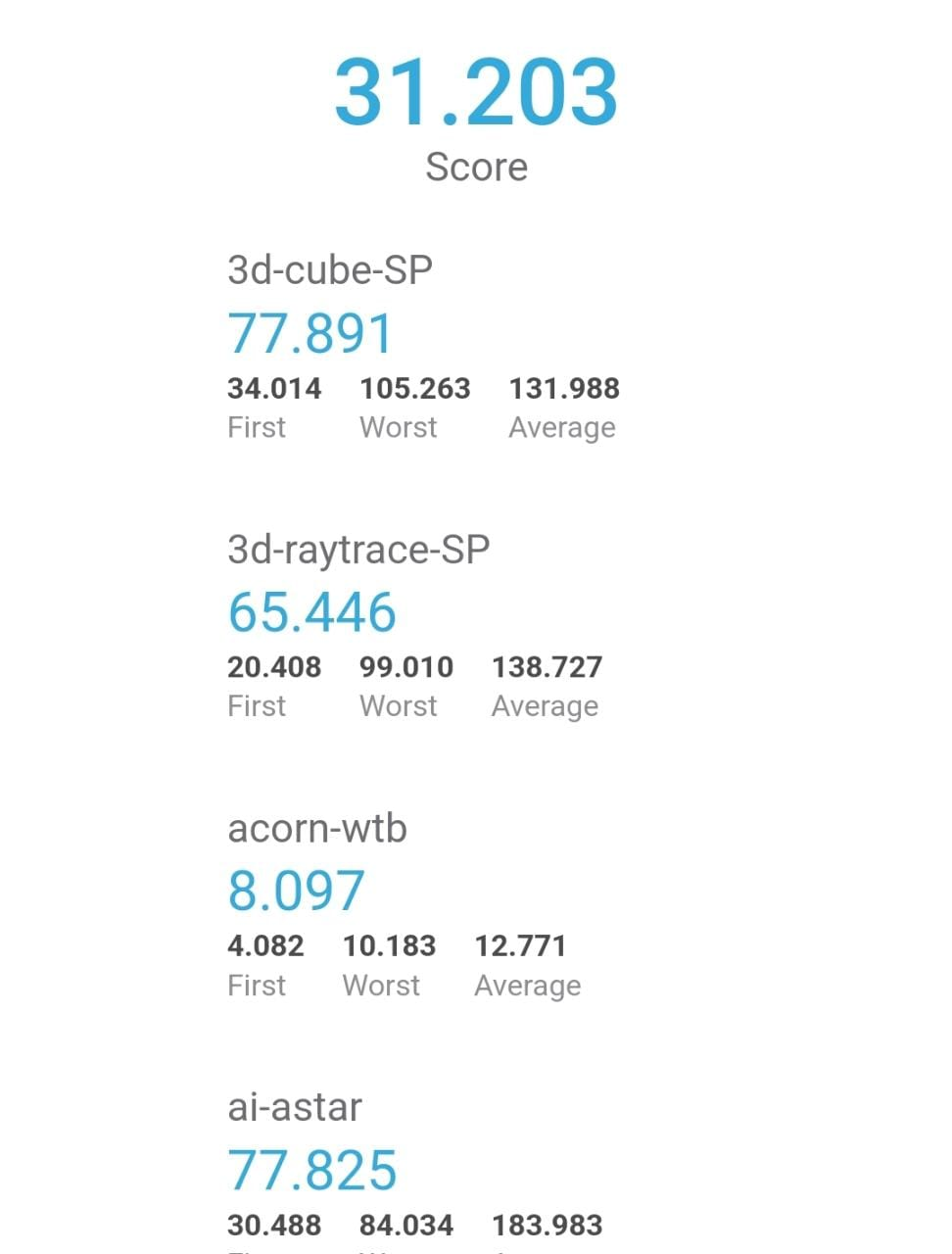
The above benchmark test runs through a couple of intense tests that cover almost all aspects of user experience and gives you an average score at the end. For the initial test that we ran without any optimizations, the Score was 31.203
Let’s now have a look at the 3 tips you can use to improve the performance of your PhoneGap/Cordova application
Tip 1: Using Crosswalk WebView in a Phonegap application

After all of the introduction, you may have a few guesses as to what causes these performance slowdowns. And if you guessed System Webview then you are right.
System Webview is known to be generally slow & non-dependable. The implementation of Webview also varies from device to device. This can cause code to be unreliable and have varied performance on different devices
So let’s start with the easiest but most effective way of improving the performance – Changing the Webview
Yep, that’s right, we are going to ditch the default System Webview in favor of Crosswalk webview, now there are a few benefits & downsides to making this change
Benefits
- Crosswalk is built specifically keeping performance in mind
- It runs the same on all devices since we are not depending upon the system implementation of the Webview
Downsides
- Since we are embedding an entire implementation of review inside the application this might increase the app size by ~15Mb, but this is not much of a problem looking at the performance improvements this provides
To install Crosswalk Webview in a Cordova Project
- Navigate to the folder where the Cordova project is located, and run the following command
cordova plugin add cordova-plugin-crosswalk-webview- The above command should automatically install Crosswalk Webview into the project without any additional setup
- Now, rebuild the application by running Cordova build
cordova build androidAnd that’s it! Within a few minutes, we replaced the default System Webview with that of Crosswalk. This should now create huge performance improvements which we’ll be measuring later
Tip 2: Using FastClick to improve Responsiveness of Phonegap application

This tip is not so much about improving the performance of the Cordova app but more about making the app feel more responsive and smooth.
The problem with most Older WebView Implementations is that they add a 300-millisecond delay between the user click and the actual click being registered onto the device. This is done to properly register double taps.
But in reality, a delay of 50-100 milliseconds should get the job done and that’s exactly why a library called fast click was made to circumvent this situation.
To integrate fast click to your Cordova/Phonegap application
- Download the latest fastclick.js library file from this official GitHub page https://github.com/ftlabs/fastclick
- Move the downloaded fastclick.js file inside your project folder and include it in the project by adding a <script> tag as shown below
<script src='js/fastclick.js'></script>- You can “attach” fast click to any part of your website as required, but for the best results, it’s recommended to use Fastclick on the whole website by attaching it to the root level <body> element
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function() {
FastClick.attach(document.body);
}, false);And done! Try recompiling the application and you should now notice that the touches/taps feel a lot more responsive and native-like than before
Tip 3: Web Optimizations to Improve the “performance” of Phonegap application

Since Phonegap/Cordova mainly runs the Website Code written in HTML/CSS/JavaScript, optimizing that should certainly make the application feel & perform faster. Therefore in this section, instead of optimizing Cordova, we’ll be looking at a few tweaks to make the Web Part of the application faster which will in turn make the app faster
Making fewer layout updates
The fewer the layout updates, the less there will be a chance of expensive re-renders and even less there will be a chance of Frame drops / Lag
This can be done by batching the layout changes into one and pushing all of them at the same time so that multiple updates can be processed in a single re-render.
A good example of this would be a Todo List Application where you have to re-render the List as soon as someone adds a new task. Normally, to render an entire list of tasks we run a for loop and append the task elements one by one.
One way to reduce the re-renders, in this case, would be to create a new element and add all of the tasks to it and only append the new element once.
Be vary of Memory Leaks

Nothing causes the app to slow down more quickly than having multiple memory leaks. The main culprit of memory leaks is having open listeners or open database connections.
The best way to avoid these memory leaks is to keep track of all of the possible sources of leaks and make sure that they are disposed of / cleaned properly if they are not required
Avoid CSS Gradients

This might seem a bit odd at first, but it’s true, CSS Gradients can slow down the rendering of the application as it has to render multiple colors and most browser rendering engines are not optimized for this.
Instead, use Static Images wherever CSS Gradients are required as they are more performant.
Prefer CSS Animations instead of JavaScript

CSS Transitions and Animations are generally faster and feel smoother when compared to manual animations made by altering the properties ( height, rotation, width , etc ) in JavaScript
This is because most browsers and WebView Implementations optimize the CSS Transitions but there are no such default optimizations for manually created JavaScript animations.
Conclusion
We took a look at quite a lot of methods to optimize the app and covered almost every area where optimization was possible.
After doing all of that, let’s check if it was worth it and try to run the benchmark test again.
Here are the final results of the Jetstream2 Benchmark after finishing the improvements
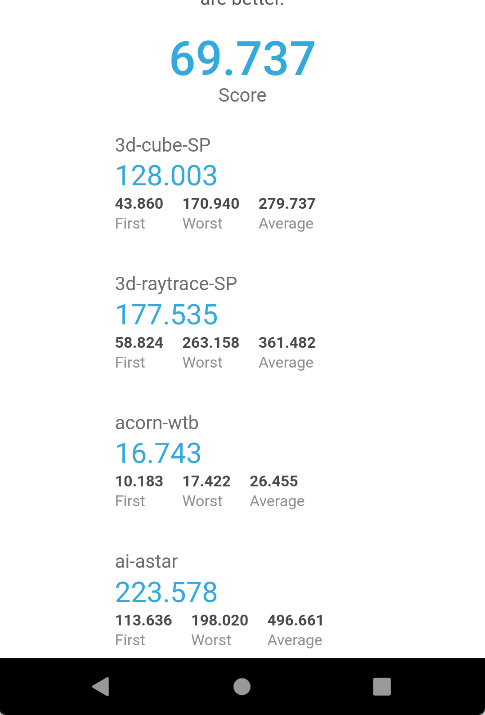
Impressive! A total of 123.495% increase should surely make the app feel a lot more smoother and responsive on most mobile devices, in fact, most users with relatively modern devices probably won’t even notice a difference between a Heavily Optimized Cordova App and a Native Application. But it is a fact that Hybrid Apps will still be behind native applications in one way or another. So it’s only recommended to go for Hybrid Apps if multi-platform development is a requirement and you can compromise on performance a little bit.
